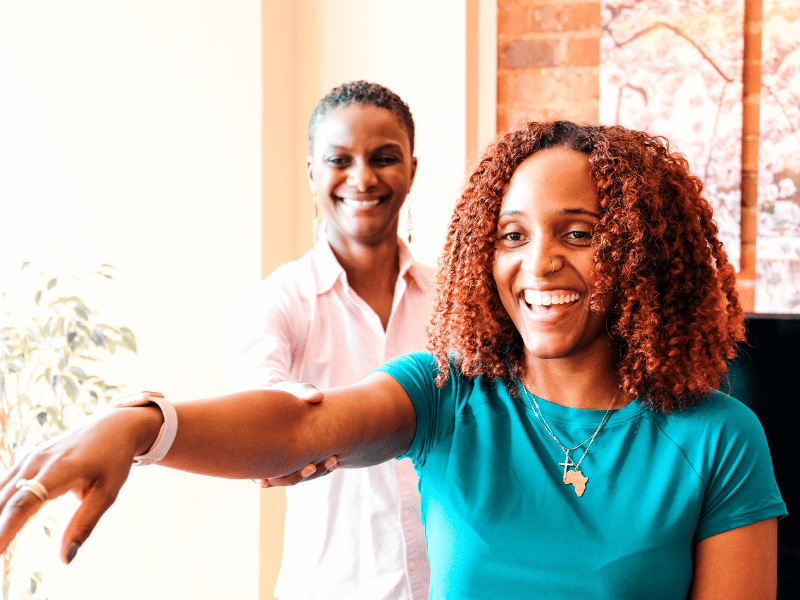Effective Hip Pain Relief: Proven Strategies for a Pain-Free Life
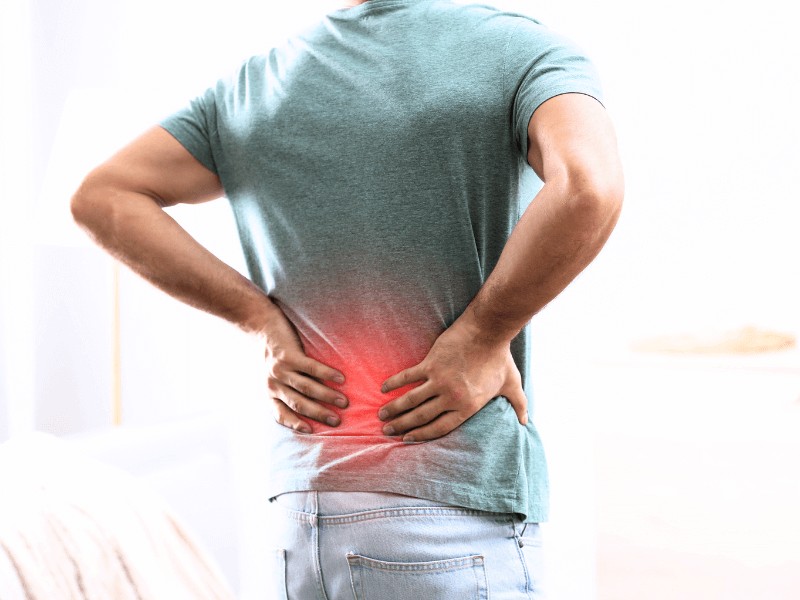
Hip pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages—making everyday activities like walking, sitting, and sleeping uncomfortable and, for some, extremely challenging. Whether it arises from overuse, injury, or underlying health conditions, hip pain can significantly impact your quality of life.
Studies show that a substantial portion of the population will experience this discomfort at some point in their lives. For instance, a systematic review published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy highlighted that up to 10% of individuals will suffer from hip pain at some stage, and that number will increase as they age (1).
Nobody should have to live with the constant discomfort and limitations that hip pain can impose. Whether you're a weekend warrior, a competitive athlete, or someone just looking to enjoy a leisurely walk without discomfort, hip pain can significantly hamper your lifestyle. There's good news—effective treatment options and preventative strategies exist, capable of not only alleviating pain, but also improving overall hip function and quality of life.
This article will guide you through the essential knowledge about hip pain, including its causes, symptoms, and, most importantly, the proven strategies for relief. From cutting-edge medical treatments to tried-and-true physical therapy techniques, we will explore a comprehensive approach to managing hip pain. You'll be empowered with the information needed to take the first steps toward a pain-free life.
Your journey toward better health and mobility starts here.
What is Hip Pain?
Hip pain can range from mild, nagging discomfort to severe, debilitating pain that can impede mobility, stability, and strength. It might be felt directly over the hip, in the groin area, or even radiate down the thigh or leg, affecting how one walks, sits, and even sleeps.
Hip pain is the body's way of signaling that something is amiss within or around the hip joint. The hip joint itself is a marvel of engineering, designed for both stability and a wide range of motion. It's a ball-and-socket joint, where the head of the femur (thighbone) fits into the acetabulum, a cup-shaped socket in the pelvis. This configuration, supported by a complex arrangement of muscles, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, allows for a wide variety of movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
However, this intricate balance can be disrupted by various factors. Pain can arise from acute injuries, such as falls or direct impacts, overuse injuries from repetitive motion, or chronic conditions including arthritis and bursitis.
Symptoms of Hip Pain
Hip pain manifests in various ways, depending on the cause, severity, and the individual's overall health. Recognizing the symptoms is the first step toward seeking effective treatment and returning to a more comfortable, active lifestyle.
Here's a detailed and comprehensive list of symptoms frequently associated with hip pain. Keep in mind that experiencing one or more of these symptoms doesn't necessarily mean you have a severe condition, but it may be a sign to consult a healthcare professional like a physical therapist for a thorough evaluation:
- Localized Pain: Discomfort or aching located in the hip joint, groin, thigh, or buttocks. This pain might be sharp during activity and dull when at rest.
- Radiating Pain: Pain that spreads from the hip to the lower back, thigh, or even down to the knee, often indicating nerve compression or irritation.
- Stiffness: A feeling of restricted movement in the hip joint, especially noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Swelling and Tenderness: The hip area may become swollen or tender to the touch, potentially indicating inflammation or injury.
- Limping: Difficulty walking normally due to discomfort or stiffness in the hip.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty performing movements that involve the hip, such as bending, twisting, or walking.
- Clicking or Catching Sensation: Some individuals report a feeling of the hip "catching" or "clicking" during movement.
- Weakness in the Hip or Leg: A feeling of reduced strength in the muscles around the hip or leg, affecting stability and mobility.
- Pain During Specific Activities: Certain actions may exacerbate pain, like climbing stairs, standing from a seated position, or lying on the affected side.
It's crucial to listen to your body and seek medical attention if hip pain persists, worsens, or impacts your ability to engage in everyday activities. A healthcare professional can help determine the cause of your symptoms and develop a personalized treatment plan to address them.
Causes of Hip Pain
Hip pain is a symptom that can arise from a multitude of factors, each contributing to discomfort in different ways. It's essential to understand that while these risk factors are frequently associated with hip pain, their presence does not guarantee the development of the condition. Rather, they indicate a potential vulnerability or predisposition to experiencing symptoms.
Here are common causes and risk factors that may contribute to hip pain:
- Osteoarthritis: Often associated with aging, osteoarthritis is caused by wear and tear on the hip joint, leading to inflammation, pain, and reduced mobility.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that can attack the lining of the hip joint, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint, can lead to sharp, shooting pain or a dull, constant ache.
- Tendinitis: Overuse or strain can inflame the tendons around the hip joint.
- Muscle or Tendon Strain: Repeated activities and overuse can strain the muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the hips.
- Hip Fractures: Bones weakened by osteoporosis or other conditions may fracture during falls or accidents, causing severe hip pain.
- Labral Tear: The labrum, a ring of cartilage surrounding the socket of the hip joint, can tear due to injury or overuse.
- Avascular Necrosis: Disruption of blood flow to the hip bone can lead to bone death and hip pain.
- Infections: Infections within the joint or bone can lead to pain, swelling, and fever.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle may contribute to weakening of the muscles around the hip and reduced flexibility, potentially leading to discomfort and pain over time.
- Overactivity: Conversely, engaging in high-intensity activities without proper conditioning or rest can put excessive stress on the hip, leading to pain.
- Obesity: Excessive body weight can increase stress on the hip joint, contributing to the development of hip pain over time.
- Back issues: Something we sometimes overlook is the referral of the back to the hip. Sometimes the hip pain is a tricky indicator that the back is injured.
Understanding these risk factors and how they potentially contribute to hip pain is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. It's always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment and tailored advice, especially if hip pain persists or impacts your quality of life.
Treatment Options for Hip Pain
Managing hip pain effectively requires a multifaceted approach, tailored to the individual's specific condition, severity of symptoms, and overall health. Treatment strategies range from conservative, non-invasive methods to more intensive interventions, including surgery. The goal is to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. Here's an overview of the various treatment options for hip pain:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) can reduce pain, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve), may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy for hip pain aims to strengthen the muscles around the hip, improve flexibility, and increase range of motion. Therapists may use techniques like stretching, manual therapy, and personalized exercise programs to address specific needs and goals.
- Exercise and Weight Management: Regular, low-impact exercises—such as swimming, cycling, and yoga—can strengthen the muscles that support the hip joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight can also relieve pressure on the hips.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying ice packs can reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, while heat therapy can relax tight muscles and improve circulation. Alternating between hot and cold therapy may offer additional relief for some individuals.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the hip joint or surrounding tissues can provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation and pain. Hyaluronic acid injections may also be considered to improve joint lubrication and ease discomfort.
- Assistive Devices: Walking aids like canes or walkers can help take the weight off the affected hip, improving mobility and reducing pain during the healing process.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments have not provided relief, or if the hip joint is significantly damaged, surgery may be considered.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy are alternative treatments that some people find helpful for managing hip pain, although more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness.
Each of these treatment options has its place in the management of hip pain, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Physical therapy, in particular, offers a broad spectrum of benefits beyond pain relief, including improved mobility, prevention of future injuries, and enhanced ability to perform daily activities.
How Physical Therapy for Hip Pain Can Help
Physical therapy stands out as a highly effective approach to managing and treating hip pain. By working with a skilled physical therapist to treat hip pain, individuals can embark on a personalized treatment journey tailored to their specific needs, underlying causes of pain, and personal health goals.
A specialized physical therapist will begin by conducting a thorough evaluation, which may include assessing your walking pattern, hip mobility, strength, and how your pain affects daily activities. This comprehensive assessment allows the therapist to identify the contributing factors to your hip pain and design a targeted treatment plan. The core of physical therapy for pain in the hip involves a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and education.
Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization, are used to improve joint mobility, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. These hands-on techniques help to restore movement in stiff joints and relax tight muscles.
Therapeutic exercise is another essential element of effective physical therapy for hip pain. Unlike general exercise, these are carefully selected and customized exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles around the hip, improving flexibility, and increasing range of motion. These exercises not only support the hip joint but also contribute to overall stability and mobility, significantly reducing the risk of future injuries.
Education also plays a pivotal role in the physical therapy process. Therapists provide valuable insights into proper posture, body mechanics, and ergonomics, which are essential for protecting the hip joint during daily activities. Furthermore, patients learn about self-management techniques, including specific stretches and exercises, to maintain their gains and prevent the recurrence of pain.
Working with a skilled physical therapist offers a dynamic and interactive approach to treating pain in your hip. It's a partnership where your input and feedback help to refine the treatment plan, ensuring it aligns with your evolving needs and goals. Through this collaborative effort, physical therapy for hip pain not only seeks to relieve pain but also empowers individuals to lead a more active, fulfilling life without the limitations of hip pain.
Our Top Exercises & Stretches for Hip Pain
Managing pain around the hip effectively often involves a combination of exercises and stretches that target the muscles around the hip joint. These exercises are designed to improve flexibility, strength, and overall joint function, contributing significantly to pain relief and mobility enhancement. Here are three beneficial exercises and stretches, each with step-by-step instructions:
1. Hip Flexor Stretch
- Start by kneeling on a soft surface. Step forward with one foot, so you're in a lunge position, with your forward knee bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Keep your back straight and gently push your hips forward until you feel a stretch in the front of your hip on the kneeling side. Ensure your forward knee does not extend past your toes.
- Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat. Perform this stretch 2-3 times on each side.
2. Glute Bridges
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground, hip-width apart. Rest your arms by your sides, palms down.
- Squeeze your glutes and lift your hips towards the ceiling, creating a straight line from your shoulders to your knees. Ensure your core is engaged and your back remains straight.
- Hold the lifted position for a few seconds, then slowly lower your hips back to the starting position.
- Repeat 10-15 times, for 2-3 sets.
3. Seated Piriformis Stretch
- Sit on a chair and cross one leg over the other so that your ankle rests on the opposite knee.
- Gently lean forward while keeping your back straight, increasing the stretch as you feel a gentle tension in the gluteal area of the crossed leg.
- Hold this position for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat. Perform this stretch 2-3 times on each side.
These exercises and stretches are generally safe and effective for managing hip pain. However, it's crucial to perform them with proper form to avoid injury and achieve the best results. If any exercise or stretch causes pain or discomfort, stop immediately.
Disclaimer: Before starting any exercise program, especially if you're dealing with hip pain or any other health condition, it's advisable to consult with a MovementX physical therapist. A qualified professional can assess your specific needs and ensure that the exercises and stretches you undertake are safe and effective for your particular situation.
Prevention of Hip Pain
Preventing hip pain or reducing the risk of its occurrence involves adopting lifestyle changes and incorporating specific practices into your daily routine. These strategies focus on maintaining the health and functionality of the hip joint and the surrounding muscles.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the hips, which can accelerate joint wear and tear or exacerbate pain. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce this strain.
- Strengthen Muscles: Strong muscles around the hips and core support the hip joint and can prevent injuries. Incorporate exercises that target the hip abductors, flexors, and extensors, as well as the lower back and core muscles, into your routine.
- Stay Active: Regular, moderate exercise improves joint health by increasing blood flow and keeping the supporting muscles strong. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options as they are low impact yet effective for hip strength and flexibility.
- Flexibility Exercises: Stretching the muscles around the hips can improve your range of motion and reduce the risk of strains and sprains. Regularly include flexibility exercises in your routine, focusing on the hip flexors, hamstrings, and piriformis muscles.
- Proper Posture and Ergonomics: Maintaining good posture and ergonomics, especially if you have a sedentary job, can prevent undue stress on the hips. Use chairs that support your lower back, keep your feet flat on the floor, and take frequent breaks to walk and stretch.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Shoes that provide proper support can improve your posture and reduce the risk of hip and lower back pain. Avoid high heels and shoes with inadequate support, especially during long periods of standing or walking.
- Avoid Overuse: While staying active is essential, it's equally important to avoid overuse of the hip joint. Listen to your body and allow time for recovery, especially after intense activities or workouts.
- Learn Proper Techniques: If you're involved in sports or physical activities, ensure you're using the correct techniques to avoid unnecessary stress on your hips. Consider working with a coach or trainer who can provide personalized guidance.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: If you have conditions that can affect the hips, such as arthritis or diabetes, managing these effectively can help prevent associated hip pain. Regular check-ups and following your healthcare provider's advice are crucial.
By integrating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can effectively reduce the risk of hip pain or prevent its recurrence. Remember, consistency is key, and making small changes over time can lead to significant improvements in hip health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In exploring the multifaceted nature of hip pain, we've covered its symptoms, causes, and a wide array of treatment options, with a special focus on the transformative role of physical therapy.
As you reflect on your own journey, consider the following questions: Are there changes you could make today that might improve your hip health? Have you explored all the potential strategies that could alleviate your pain and restore your mobility?
If hip pain is affecting your daily life, know that you don't have to navigate this path alone. MovementX offers personalized, expert-guided physical therapy tailored to your unique situation and goals. Our skilled therapists are ready to work with you, providing the support, knowledge, and encouragement you need to overcome hip pain.
Don't let hip pain hold you back from the activities you love or the life you deserve to live. Request a session with MovementX today, and take the first step toward a more active, fulfilling, and pain-free life.
Your journey to recovery and beyond starts with a single step. Are you ready to take it?
References
- J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Oct-Dec; 36(4): 450–457. Published online 2020 Sep 26. doi: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_170_19
Share This Page
More Conditions We Treat
Found this page interesting? Learn more about other conditions we treat: